●试题四阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】函数QuickSort是在一维数组A[n]上进行快速排序的递归算法。【函数】void QuickSort(int A[],int s,int t){int i=s,j=t+1,temp;int x=A[s];do{do i++;while (1) ;do j--;while(A[j]x);if(ij){temp=A[i]; (2) ; (3) ;}}while(ij);A[a]=A[j];A[j]=x;if(si-1) (4) ;if(j+1t) (5) ;}
●试题一阅读下列函数说明和C代码,把应填入其中n处的字句写在答卷的对应栏内。【函数1.1说明】函数strcpy(char*to,char*from)将字符串from复制到字符串to。【函数1.1】void strcpy(char*to,char*from){while( ( 1 ) );}【函数1.2说明】函数merge(int a[ ],int n,int b[ ],int m,int *c)是将两个从小到大有序数组a和b复制合并出一个有序整数序列c,其中形参n和m分别是数组a和b的元素个数。【函数1.2】void merge(int a[ ],int n,int b[ ],int m,int *c){ int i,j;for(i=j=0;i<n j<m;)*c++=a[i]<b[j]? a[i++]:b[j++];while( (2) )*c++=a[i++];while( (3) )*c++=b[j++];}【函数1.3说明】递归函数sum(int a[ ],int n)的返回值是数组a[ ]的前n个元素之和。【函数1.3】int sum(int a[ ],int n){ if(n>0)return (4) ;else (5) ;}
试题八(共15分)阅读以下说明和Java程序代码,将应填入(n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。[说明]在下面的 Java 程序代码中,类SalesTicket 能够完成打印票据正文的功能,类HeadDecorator 与FootDecorator 分别完成打印票据的台头和脚注的功能。已知该程序运行后的输出结果如下所示,请填补该程序代码中的空缺。这是票据的台头!这是票据正文!这是票据的脚注!------------------------这是票据的台头!这是票据的脚注![Java程序代码]public class SalesTicket {public void printTicket() {System.out.println("这是票据正文!");}}public class Decorator extends SalesTicket{SalesTicket ticket;}}public class FootDecorator extends Decorator{public FootDecorator(SalesTicket t) {(2) ;}public void printTicket() {super.printTicket();System.out.println("这是票据的脚注!");}}public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {T = new HeadDecorator( (3) );T. (4) ;System.out.println("------------------------");T = new FootDecorator( (5) );T.printTicket();}}public Decorator(SalesTicket t){ticket = t;}public void printTicket(){if(ticket != null)ticket.printTicket();}}public class HeadDecorator extends Decorator{public HeadDecorator(SalesTicket t) {(1) ;}public void printTicket() {System.out.println("这是票据的台头!");super.printTicket();
阅读以下说明和流程图,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】已知头指针分别为La和lb的有序单链表,其数据元素都是按值非递减排列。现要归并La和Lb得到单链表Lc,使得Lc中的元素按值非递减排列。程序流程图如下所示:
阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】函数QuickSort是在一维数组A[n]上进行快速排序的递归算法。【函数】void QuickSort( int A[ ],int s,int t){ int i=s,j=t+1,temp;int x=A[s];do{do i ++ ;while (1);do j -- ;while(A[j]>x);if(i<j){temp=A[i];(2);(3);}}while(i<j);A[a] =A[j];A[j] =x;if(s<i-1) (4);if(j+1<t) (5);}
阅读以下说明和流程图,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。[说明]设学生某次考试的成绩按学号顺序逐行存放于某文件中,文件以单行句点“.”为结束符。下面的流程图读取该文件,统计出全部成绩中的最高分max和最低分min。
阅读下列说明和流程图,将应填入(n)的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】下列流程图(如图4所示)用泰勒(Taylor)展开式sinx=x-x3/3!+x5/5!-x7/7!+…+(-1)n×x2n+1/(2n+1)!+…【流程图】计算并打印sinx的近似值。其中用ε(>0)表示误差要求。
阅读以下说明和c++码,将应填入(n)处的字名写在的对应栏内。[说明] 以下函数完成求表达式的值,请填空使之完成此功能。float sum ( float x ){ float s=0.0;int sign = 1;(1);for(inti=1;(2); i+ +){t=t*x;s=s+(3);sign = - sign;(4);}
阅读下列说明和流程图,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。【说明】下列流程图用泰勒(Taylor)展开式y=ex=1+x+x2/2!+x3/3!+…+xn/n!+…计算并打印ex的近似值,其中用ε(>0)表示误差要求。【流程图】
阅读以下说明,以及用C++在开发过程中所编写的程序代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】在下面函数横线处填上适当的字句,使其输出结果为:构造函数.构造函数.1,25,6析构函数析构函数.【C++代码】include "iostream.h"class AA{ public;AA(int i,int j){A=i; B=j;cout<<"构造函数.\n";}~AA(){(1);}void print();private:int A, B;};void AA∷print(){cout<<A<<","<<B<<endl;}void main(){AA *a1, *a2;(2)=new AA(1, 2);a2=new AA(5, 6);(3);a2->print();(4) a1;(5) a2;}
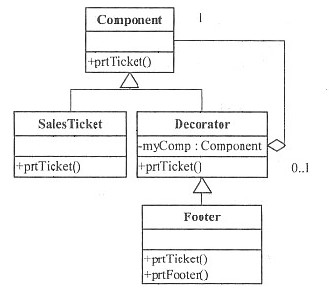
阅读以下说明和Jrdva代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。[说明]在销售系统中常常需要打印销售票据,有时需要在一般的票据基础上打印脚注。这样就需要动态地添加一些额外的职责。如下展示了Decorator(修饰)模式。SalesOrder对象使用一个SalesTicket对象打印销售票据。图6-1显示了各个类间的关系。以下是Java语言实现,能够正确编译通过。[图6-1][Java代码]//Component.java文件public (1) class Component {abstract publ ic void prtTicket();}//salesTicket.java文件public class SalesTicket extends Component{public void prtTicket(){//Sales ticket printing code hereSystem.out.printin("SalesTicket");}}//Decorator.java文件publ ic abstract class Decorator extends Component{public void prtTicket(){if(myComp!=null)myComp.prtTicket();}private (2) myComp;public Decorator(Component myC){myComp=myC;}}//Footer.java文件public class Footer extends Decorator {public Footer(Component myC){(3);}public void prtTicket(){(4);prtFooter();}publ ic void prtFooter(){//place printing footer code hereSystem.out.println("Footer");}}//salesorder.java文件public class SalesOrder{void prtTicket(){Component myST;myST=new Footer( (5) );//Print Ticket with footers as neededmyST.prtTicket();}}(1)
阅读下列程序说明和C++程序,把应填入其中(n)处的字句,写在对应栏内。【说明】阅读下面几段C++程序回答相应问题。比较下面两段程序的优缺点。①for (i=0; i<N; i++ ){if (condition)//DoSomething…else//DoOtherthing…}②if (condition) {for (i =0; i<N; i++ )//DoSomething}else {for (i=0; i <N; i++ )//DoOtherthing…}
试题五(共15分)阅读下列说明和C++-代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某发票(lnvoice)由抬头(Head)部分、正文部分和脚注(Foot)部分构成。现采用装饰( Decorator)模式实现打印发票的功能,得到如图5-1所示的类图。【C++代码】include iostreamusing namespace std;class invoice{public:(1) {cout《 This is the content of the invoice!《 endl;}};class Decorator : public invoice {Invoice *ticket;public:Decorator(lnvoice *t) { ticket = t; }void printinvoice(){if(ticket != NULL)(2);}};class HeadDecorator : public Decorator{public:HeadDecorator(lnvoice*t): Decorator(t) { }void printinvoice0 {cout《 This is the header of the invoice! endl;(3) ;}};class FootDecorator : public Decorator{public:FootDecorator(invoice *t): Decorator(t) { }void printlnvoice() {(4) ;cout《 This is the footnote of the invoice!《 endl;}};int main(void) {Invoice t;FootDecorator f(t);HeadDecorator h(f);H.printlnvoice();cout “_____” endl;FootDecorator a(NULL);HeadDecorator b( (5) );B.printinvoice();return 0;}程序的输出结果为:This is the header of the invoice!This is the content of the invoice!This is the footnote of the invoice!----------------------------This is the header of the invoice!This is the footnote of the invoice!
试题六(共15分)阅读下列说明和Java代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某发票(lnvoice)由抬头(Head)部分、正文部分和脚注(Foot)部分构成。现采用装饰( Decorator)模式实现打印发票的功能,得到如图6-1所示的类图。【java代码】class invoice{public void printInvoice(){:System.out.println ( This is the content of the invoice!);}}class Decorator : extends Invoice {protected Invoice ticket;public Decorator(lnvoice t){ticket = t;}public void printinvoice(){if(ticket != NULL)(1);}}class FootDecorator extends Decorator{public FootDecorator(lnvoice t){super(t);}public void printinvoice (){Systent.out.println( This is the header of the invoice! );(2) ;}}class FootDecorator extends Decorator {public FootDecorator(invoice t):{super(t);}public void printlnvoice(){(3) ;Systent.out.println( This is the header of the invoice! );}}Class test {public static void main(string[] args){Invoice t =new invioce();Invoice ticket;Ticket= (4) ;Ticket. Printinvoice();Systent.out.println(“--------------“)Ticket= (5) ;Ticket. Printinvoice();}}程序的输出结果为:This is the header of the invoice!This is the content of the invoice!This is the footnote of the invoice!----------------------------This is the header of the invoice!This is the footnote of the invoice!
阅读下列说明和c++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某灯具厂商欲生产一个灯具遥控器,该遥控器具有7个可编程的插槽,每个插槽都有开关按钮,对应着一个不同的灯。利用该遥控器能够统一控制房间中该厂商所有品牌灯具的开关,现采用Command(命令)模式实现该遥控器的软件部分。Command模式的类图如图5-1所示。【c++代码】}
●试题二阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】该程序运行后,输出下面的数字金字塔【程序】includestdio.hmain (){char max,next;int i;for(max=′1′;max=′9′;max++){for(i=1;i=20- (1) ;++i)printf(" ");for(next= (2) ;next= (3) ;next++)printf("%c",next);for(next= (4) ;next= (5) ;next--)printf("%c",next);printf("\n");}}
●试题一阅读下列说明和流程图,将应填入(n)的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】下列流程图(如图4所示)用泰勒(Taylor)展开式sinx=x-x3/3!+x5/5!-x7/7!+…+(-1)n×x 2n+1/(2n+1)!+…【流程图】图4计算并打印sinx的近似值。其中用ε(0)表示误差要求。
试题三(共 15 分)阅读以下说明和 C 程序,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
(a)智能网概念模型中分布功能平面模型如下图所示,请根据此图将应填入(n)处的 字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
阅读以下说明和C++程序代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】在下面的C++代码中,类SalesTicket能够完成打印票据正文的功能,类HeadDec- orator与FootDecorator分别能够完成打印票据的台头和脚注的功能。已知该程序运行后的输出结果如下所示,请填补该程序代码中的空缺。这是票据的台头!这是票据正文!这是票据的脚注!---------------这是票据的台头!这是票据的脚注!【C++程序代码】#includeusing namespace std;class SalesTicket {public:(1) printTicket() { cout " 是票据正文!" endl;}class Decorator : public SalesTicket{SalesTicket *ticket;public:Decorator(SalesTicket *t){ ticket = t; }void printTicket(){if(ticket != NULL)ticket->printTicket();}};class HeadDecorator : public Decorator{public:HeadDecorator(SalesTicket *t): (2) { }void printTicket() {sour "这是票据的台头!" endl;Decorator::printTicket();}};class FootDecorator :public Decorator{public:FootDecorator(SalesTicket *t): (3)void printTicket() {Decorator::printTicket();cout "这是票据的脚注!" endl;}};void main(void) {SalesTicket t;FootDecorator f(t);HeadDecorator h( (4) );h.printTicket();cout "-------------------------" endl;FootDecorator a(NULL);HeadDecorator b( (5) );b.printTicket();}
阅读下列说明和 C ++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某软件公司欲开发一款汽车竞速类游戏,需要模拟长轮胎和短轮胎急刹车时在路面上留 下的不同痕迹,并考虑后续能模拟更多种轮胎急刹车时的痕迹。现采用策略(Strategy)设计模式来实现该需求,所设计的类图如图 6-1 所示。【C++ 代码】#includeusing namespace std;class BrakeBehavior{public:(1) ; /*其余代码省略*/};class LongWheelBrake : public BrakeBehavior{public:void stop(){cout
阅读下列说明和C++-代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。 【说明】 某发票(lnvoice)由抬头(Head)部分、正文部分和脚注(Foot)部分构成。现采用装饰(Decorator)模式实现打印发票的功能,得到如图5-1所示的类图。【C++代码】 #include using namespace std; class invoice{ public: (1){ cout
阅读下列说明和C++代码,回答问题,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某航空公司的会员积分系统将其会员划分为:普卡 (Basic)、银卡(Silver)和金卡 (Gold) 三个等级。非会员 (NonMember) 可以申请成为普卡会员。会员的等级根据其一年内累积 的里程数进行调整。描述会员等级调整的状态图如图 5-1 所示。现采用状态 (State) 模式实现上述场景,得到如图 5-2 所示的类图。【问题1】(15分)阅读上述说明和C++代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
阅读下列说明和 Java 代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。 【说明】 某软件公司欲开发一款汽车竞速类游戏,需要模拟长轮胎和短轮胎急刹车时在路面上 留 下的不同痕迹,并考虑后续能模拟更多种轮胎急刹车时的痕迹。现采用策略(Strategy) 设 计模式来实现该需求,所设计的类图如图 5-1 所示。
阅读下列说明和C++-代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】 某发票(lnvoice)由抬头(Head)部分、正文部分和脚注(Foot)部分构成。现采用装饰( Decorator)模式实现打印发票的功能,得到如图5-1所示的类图。【C++代码】#includeusingnamespace std;class Invoice{public: (1) { coutinvoice!" }};classDecorator : public Invoice { Invoice *ticket;public: Decorator(lnvoice *t) { ticket = t; } void printInvoice( ){ if(ticket != NULL) (2); } };classHeadDecorator : public Decorator{public: HeadDecorator(lnvoice*t): Decorator(t) { } void printInvoice( ) { coutheader of the invoice! " (3) ; } }; class FootDecorator : public Decorator{ public: FootDecorator(Invoice *t): Decorator(t) { } void printlnvoice( ){ (4) ; coutfootnote of the invoice!" }};int main(void){ Invoice t; FootDecorator f( HeadDecorator h( h.printInvoice( ); cout FootDecorator a(NULL) ; HeadDecorator b( (5) ); b.printInvoice( ); return 0;}程序的输出结果为: This is the header of the invoice! This is the content of the invoice! This is the footnote of the invoice! ---------------------------- This is the header of the invoice! This is the footnote of the invoice!
阅读下列说明和Java代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】 某文件管理系统中定义了类OfficeDoc和DocExplorer,当类OfficeDoc发生变化时,类DocExplorer的所有对象都要更新其自身的状态,现采用观察者(Observer)设计模式来实现该需求,所设计的类图如图6-1所示。
阅读下列说明和?C++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】阅读下列说明和?Java代码,将应填入?(n)?处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某快餐厅主要制作并出售儿童套餐,一般包括主餐(各类比萨)、饮料和玩具,其餐品种类可能不同,但其制作过程相同。前台服务员?(Waiter)?调度厨师制作套餐。现采用生成器?(Builder)?模式实现制作过程,得到如图?6-1?所示的类图。