有以下程序:程序运行后的输出结果是( )。A.10,One*Dream!B.9,One*Dream!C.9,One*WorldD.10,One*World
有以下程序:
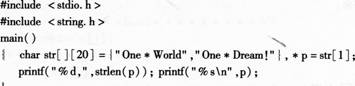
程序运行后的输出结果是( )。
A.10,One*Dream!
B.9,One*Dream!
C.9,One*World
D.10,One*World
相关考题:
有以下程序#include stdio.h#include string.hmain(){ char str[ ][20]={"One*World","One*Dream!"},*p=str[1];printf("%d,",strlen(p));printf("%s\n",p);}程序运行后的输出结果是A)9,One*WorldB)9,One*Dream !C)10,One*Dream !D)10,One*World
( 10 )执行下列程序,显示的结果是 【 10 】 。one= "WORK"two = ""a = LEN ( one )i = aDO WHILE i=1two = two + SUBSTR ( one ,i , 1 )i=i - 1ENDDO? two
有如下程序:#includeiostreamusing narnespace std;class ONE{int e;public:ONE():c(O){cout1;)ONE(int n):c(13){cout2;}};class TWO{ONE oriel;ONE one2,public:TWO(int m):one2(m){cout3;}};int main(){TWO t(4);return O;}运行时的输出结果是A.3B.23C.123D.213
有以下程序#includestdio.h#includestring.hmain( ){char str[][20]={“Qne*World”,“one*Dream!”},*P=str[1 ].prinff(“%d,”,strlen(p));printf(“%s\n”,P); ’}程序运行后的输出结果是A.9,One*World S)9,One*Dream!B.10,One*Dream!C.10,One*World
有以下程序#includestdio.h#includestring.hmain( ){char str[][20]={“Qne*World”,“one*Dream!”},*P=str[1 ].prinff(“%d,”,strlen(p));printf(“%s\n”,P); ’}程序运行后的输出结果是A.9,One*World S)B.9,One*Dream!C.10,One*Dream!D.10,One*World
有以下程序: #includestdio.h #includestring.h main( ) {char str[][20][{"One*World","One*Dream!"},*p=str[1]; prinft("%d,",strlen(p));printf("%s\n",p); } 程序运行后的输出结果是( )。A.9,0ne*WorldB.9,0ne*Dream!C.10,One*Dream!D.10,Ome*World
有以下程序:includestdio.hincludestring.hmain( ){char str[][20][{One*World,One*Dream!},*p=str[1];prinft(%d,,strlen(p));printf(%s\n,p);}程序运行后的输出结果是( )。A.9,0ne*WorldB.9,0ne*Dream!C.10,One*Dream!D.10,Ome*World
【填空题】运行下列程序,输出结果是____。 #include <iostream> using namespace std; enum opt{ONE,TWO,THREE,FOUR,FIVE,SIX,SEVEN}op; int main(void) { cout<<ONE; cout<<TWO; cout<<SIX; return 0; }