试题五(共 15分)阅读以下说明和C++代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】已知类 LinkedList 表示列表类,该类具有四个方法:addElement()、lastElement()、umberOfElement()以及removeLastElement()。四个方法的含义分别为:void addElement(Object): 在列表尾部添加一个对象;Object lastElement(): 返回列表尾部对象;int numberOfElement(): 返回列表中对象个数;void removeLastElement(): 删除列表尾部的对象。现需要借助LinkedList来实现一个Stack栈类,C++代码1和C++代码2分别采用继承和组合的方式实现。【C++代码 1】class Stack :public LinkedList{public:void push(Object o){ addElement(o); }; //压栈Object peek(){ return (1) ; }; //获取栈顶元素bool isEmpty(){ //判断栈是否为空return numberOfElement() == 0;};Object pop(){ //弹栈Object o = lastElement();(2) ;return o;};};【C++代码 2】class Stack {private:(3) ;public:void push(Object o){ //压栈list.addElement(o);};Object peek(){ //获取栈顶元素return list. (4) ;};bool isEmpty(){ //判断栈是否为空return list.numberOfElement() == 0;};Object pop(){//弹栈Object o = list.lastElement();list.removeLastElement();return o;};};【问题】若类LinkedList新增加了一个公有的方法removeElement(int index),用于删除列表中第index个元素,则在用继承和组合两种实现栈类Stack的方式中,哪种方式下Stack对象可访问方法removeElement(int index)? (5) (A. 继承 B. 组合)
●试题四阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】函数QuickSort是在一维数组A[n]上进行快速排序的递归算法。【函数】void QuickSort(int A[],int s,int t){int i=s,j=t+1,temp;int x=A[s];do{do i++;while (1) ;do j--;while(A[j]x);if(ij){temp=A[i]; (2) ; (3) ;}}while(ij);A[a]=A[j];A[j]=x;if(si-1) (4) ;if(j+1t) (5) ;}
●试题六阅读以下说明和C++程序,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】设计一个类模板Sample用于对一个有序数组采用二分法查找元素下标。【C++程序】#includeiostream.h#define Max 100∥最多元素个数templateclass Tclass Sample{T A[Max]:∥存放有序数序int n:∥实际元素个数publicSample(){}∥默认构造函数Sample(T a[],int i);∥初始化构造函数int seek(T c);void disp(){for(int i=0;in;i++)coutA[i]"";coutend1:}};templateclass TSampleT::Sample(T a[],int i){n=i;for(intj=0;ji;j++)(1) ;}templateclass Tint SampleT::seek(T c){int low=0,high=n-1,mid;while( (2) ){mid=(low+high)/2;if( (3) )return mid;else if( (4) )low=mid+l;else(5) ;}return-1;}void main(){char a[]="acegkmpwxz";Samplechars(a,1。);cout"元素序列:";s.disp();cout"元素′g′的下标:"s.seek(′g′)endl;}
●试题一阅读下列函数说明和C代码,把应填入其中n处的字句写在答卷的对应栏内。【函数1.1说明】函数strcpy(char*to,char*from)将字符串from复制到字符串to。【函数1.1】void strcpy(char*to,char*from){while( ( 1 ) );}【函数1.2说明】函数merge(int a[ ],int n,int b[ ],int m,int *c)是将两个从小到大有序数组a和b复制合并出一个有序整数序列c,其中形参n和m分别是数组a和b的元素个数。【函数1.2】void merge(int a[ ],int n,int b[ ],int m,int *c){ int i,j;for(i=j=0;i<n j<m;)*c++=a[i]<b[j]? a[i++]:b[j++];while( (2) )*c++=a[i++];while( (3) )*c++=b[j++];}【函数1.3说明】递归函数sum(int a[ ],int n)的返回值是数组a[ ]的前n个元素之和。【函数1.3】int sum(int a[ ],int n){ if(n>0)return (4) ;else (5) ;}
阅读以下说明和流程图,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】已知头指针分别为La和lb的有序单链表,其数据元素都是按值非递减排列。现要归并La和Lb得到单链表Lc,使得Lc中的元素按值非递减排列。程序流程图如下所示:
在C++标准模板库中,vector容器是一种()。 A.标准类模板B.标准类C.标准对象D.标准函数
阅读以下说明和c++码,将应填入(n)处的字名写在的对应栏内。[说明] 以下函数完成求表达式的值,请填空使之完成此功能。float sum ( float x ){ float s=0.0;int sign = 1;(1);for(inti=1;(2); i+ +){t=t*x;s=s+(3);sign = - sign;(4);}
阅读以下说明,以及用C++在开发过程中所编写的程序代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】在下面函数横线处填上适当的字句,使其输出结果为:构造函数.构造函数.1,25,6析构函数析构函数.【C++代码】include "iostream.h"class AA{ public;AA(int i,int j){A=i; B=j;cout<<"构造函数.\n";}~AA(){(1);}void print();private:int A, B;};void AA∷print(){cout<<A<<","<<B<<endl;}void main(){AA *a1, *a2;(2)=new AA(1, 2);a2=new AA(5, 6);(3);a2->print();(4) a1;(5) a2;}
阅读以下说明和Java代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】java.util库中提供了Vector模板类,可作为动态数组使用,并可容纳任意数据类型。该类的部分方法说明如下表所示:【Java代码】import (1);public class JavaMain {static private final int (2)= 6;public static void main(String[] args){Vector<Integer> theVector = new Vector< (3) >();// 初始化 theVector, 将theVector的元素设置为0至5for (int cEachItem = 0; cEachItem < ARRAY_SIZE; cEachItem++)theVector.add((4));showVector(theVector); // 依次输出theVector中的元素theVector.removeElementAt(3);showVector(theVector);}public static void showVector(Vector<Integer> theVectorif (theVector.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("theVectcr is empty.");return;}for (int loop = 0; loop < theVector.size(); loop++)System.out.print(theVector.get(loop));System.out.print(", ");}System.out.println();}}该程序运行后的输出结果为:0,1,2,3,4,5(5)
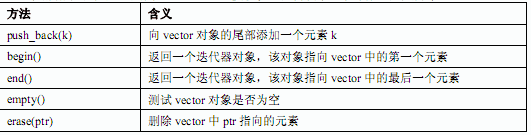
阅读以下说明和C++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。【说明】C++标准模板库中提供了vector模板类,可作为动态数组使用,并可容纳任意数据类型,其所属的命名空间为std。vector模板类的部分方法说明如下表所示:【C++代码】include <iostream>include <vector>using namespace (1);typedef vector< (2) > INTVECTOR;const int ARRAY_SIZE = 6;void ShowVector (INTVECTOR theVector);int main() {INTVECTOR theVector;// 初始化 theVector, 将theVector的元素依次设置为0至5for (int cEachItem = 0; cEachItem < ARRAY_SIZE; cEachItem++}theVector.push_back((3));ShowVector(theVector); // 依次输出theVector中的元素theVector.erase (theVector.begin () + 3};ShowVector(theVector);}void ShowVector (INTVECTOR theVector) {if (theVector.empty ()) {cout << "theVector is empty." << endl; return;}INTVECTOR::iterator (4);for (theIterator=theVector.begin(); theIterator !=theVector.end(); theIterator++) {cout << *theIterator;if (theIterator != theVector.end()-1) cout << ", ";}cout << end1;}该程序运行后的输出结果为:0,1,2,3,4,5(5)
阅读下列程序说明和C++程序,把应填入其中(n)处的字句,写在对应栏内。【说明】阅读下面几段C++程序回答相应问题。比较下面两段程序的优缺点。①for (i=0; i<N; i++ ){if (condition)//DoSomething…else//DoOtherthing…}②if (condition) {for (i =0; i<N; i++ )//DoSomething}else {for (i=0; i <N; i++ )//DoOtherthing…}
阅读下列说明和c++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某灯具厂商欲生产一个灯具遥控器,该遥控器具有7个可编程的插槽,每个插槽都有开关按钮,对应着一个不同的灯。利用该遥控器能够统一控制房间中该厂商所有品牌灯具的开关,现采用Command(命令)模式实现该遥控器的软件部分。Command模式的类图如图5-1所示。【c++代码】}
●试题二阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】该程序运行后,输出下面的数字金字塔【程序】includestdio.hmain (){char max,next;int i;for(max=′1′;max=′9′;max++){for(i=1;i=20- (1) ;++i)printf(" ");for(next= (2) ;next= (3) ;next++)printf("%c",next);for(next= (4) ;next= (5) ;next--)printf("%c",next);printf("\n");}}
试题三(共 15 分)阅读以下说明和 C 程序,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
试题七(共 15 分)阅读以下说明和 Java 代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。[说明]java.util 库中提供了 Vector 模板类,可作为动态数组使用,并可容纳任意数据类型。该类的部分方法说明如下表所示:[Java 代码]import (1) ;public class JavaMain {static private final int (2) = 6;public static void main(String[] args){VectorInteger theVector = new Vector (3) ();// 初始化 theVector,将 theVector的元素设置为 0 至 5for (int cEachItem = 0; cEachItem ARRAY_SIZE; cEachItem++)theVector.add( (4) );showVector(theVector); // 依次输出 theVector中的元素theVector.removeElementAt(3);showVector(theVector);}public static void showVector(VectorInteger theVector){if (theVector.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("theVector is empty.");return;}for (int loop = 0; loop theVector.size(); loop++) {System.out.print(theVector.get(loop));System.out.print(", ");}System.out.println();}}该程序运行后的输出结果为:0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5(5)
阅读以下说明和c++代码,将应填入 (n) 处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】c++标准模板库中提供了map模板类,该模板类可以表示多个“键一值”对的集合,其中键的作用与普通数组中的索引相当,而值用作待存储和检索的数据。此外,c++模板库还提供了pair模板类,该类可以表示一个“键-值”对。pair对象包含两个属性:first和second,其中first表示“键-值”中的“键”,而Second表示“键-值”中的“值”。map类提供了insert方法和find方法,用于插入和查找信息。应用时,将一个pair。对象插入(insert)到map对象后,根据“键”在map对象中进行查找(find),即可获得一个指向pair对象的迭代器。下面的c++代码中使用了map和pair模板类,将编号为1001、1002、1003的员工信息插入到map对象中,然后输入一个指定的员工编号,通过员工编号来获取员工的基本信息。员工编号为整型编码,员工的基本信息定义为类employee。map对象与员工对象之间的关系及存储结构如图5—1所示。【c++代码】includeincludeincludeusing namespace std;class employee {(1) :employee(string name,string phoneNumber,string address){this-name=name;this-phoneNumber=phoneNumber ;this-address=address;}string name;string phoneNumber;string address;);int main(){mapemployeeMap;typedef pairemployeeNo; //从标准输入获得员工编号map::const_iterator it;it= (5) .find(employeeNo); //根据员工编号查找员工信息if(it==employeeMap.end()){coutfirstsecond一nafae(phoneNumbersecond-address
图2-1是基于软交换的网络分层模型。请将选项应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸对应的解答栏内。
(a)智能网概念模型中分布功能平面模型如下图所示,请根据此图将应填入(n)处的 字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
图6-1是下一代网络的体系结构简图,请根据此简图将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
阅读下列说明和 C ++代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】某软件公司欲开发一款汽车竞速类游戏,需要模拟长轮胎和短轮胎急刹车时在路面上留 下的不同痕迹,并考虑后续能模拟更多种轮胎急刹车时的痕迹。现采用策略(Strategy)设计模式来实现该需求,所设计的类图如图 6-1 所示。【C++ 代码】#includeusing namespace std;class BrakeBehavior{public:(1) ; /*其余代码省略*/};class LongWheelBrake : public BrakeBehavior{public:void stop(){cout
阅读下列说明和C++-代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。 【说明】 某发票(lnvoice)由抬头(Head)部分、正文部分和脚注(Foot)部分构成。现采用装饰(Decorator)模式实现打印发票的功能,得到如图5-1所示的类图。【C++代码】 #include using namespace std; class invoice{ public: (1){ cout
试题六(共 15 分)阅读下列说明和 C++代码,填补代码中的空缺,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。【说明】以下 C++代码实现一个简单的聊天室系统(ChatRoomSystem),多个用户 (User)可以向聊天室(ChatRoom)发送消息,聊天室将消息展示给所有用户。 类图如图 6-1 所表示。 【C++代码】#include#include using namespace std; class User {private:string name; public:User(string name){ (1) =name;}~User(){} void setName(string name) {this->name=name; } string getName(){return name;}void sendMessage(string message); }; class ChatRoom { . public:static void showMessage(User* user, string message) { coutgetName()"] : " zhang->sendMessage("Hi! Leo!");li_>sendMessage("Hi! John!"); }void join(User* user) { (3) ("HeIIoEveryone!l am"+user->getName()); . ;} . };int main(){ChatRoomSystem*crs= (4) ; crs->startup();crs->join( (5) ("Wayne")); delete crs; }/* 程序运行结果: [John]:Hi! Leol [Leo]:Hi! John