下面程序的功能是建立一个有 3 个 结 点的单向循环链表,然后求各个 结 点数值域 data 中数据的和。请填空。include stdio.hinclude stdlib.hstruct NODE{ int data;struct NODE *next;};main(){ struct NODE *p,*q,*r;int sum=0;p=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));q=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));r=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));p-data=100; q-data=200; r-data=200;p- next =q; q- next =r; r- next =p;sum=p-data+p-next-data+r-next-next 【 19 】 ;printf("%d\n",sum);}
下面程序的功能是建立一个有 3 个 结 点的单向循环链表,然后求各个 结 点数值域 data 中数据的和。请填空。
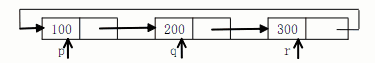
include <stdio.h>
include <stdlib.h>
struct NODE{ int data;
struct NODE *next;
};
main()
{ struct NODE *p,*q,*r;
int sum=0;
p=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
q=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
r=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
p->data=100; q->data=200; r->data=200;
p-> next =q; q-> next =r; r-> next =p;
sum=p->data+p->next->data+r->next->next 【 19 】 ;
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
相关考题:
函数 main() 的功能是 : 在带头结点的单链表中查找数据域中值最小的结点 . 请填空#include stdio.hstruct node{ int data;struct node *next;};int min(struct node *first)/* 指针 first 为链表头指针 */{ strct node *p; int m;p=first-next; m=p-data;p=p-next;for(;p!=NULL;p= _[20]_______ )if(p-datam) m=p-data;return m;}
以下程序把三 个 NODETYP E 型的变量链接成一个简单的链表 , 并 在 whil e 循环中输出链表结点数据域中的数据,请填空。#include stdio.hstruct node{int data; struct node *next;};typedef struct node NODETYPE;main(){ NODETYPE a,b,c,*h,*p;a.data=10;b.data=20;c.data=30;h=a;a.next=b;b.next=c;c.next='\0';p=h;while(p){printf("%d,", p-data); 【 1 5 】 ; }printf("\n");}
以下程序把三个NODETYPE型的变量链接成一个简单的链表,并在while循环中输出链表结点数据域中的数据,请填空#include stdio.hstruct node{int data; struct node *next;};typedef struct node NODETYPE;main(){NODETYPE a,b,c,*h,*p;a. data=10;b.data=20;c.data=30;h=a;b. next=b;b.next=c;c.next=’\0’;p=h;while(p){printf(“d”,p-data);【15】;}}
论述题 3 :针对以下 C 语言程序,请按要求回答问题( 18 分)已知 link.c 源程序如下:/*link.c 程序对单向链表进行操作 , 首先建立一个单向链表 , 然后根据用户的选择可以对其进行插入节点 、删除节点和链表反转操作 */#include#includetypedef struct list_node *list_pointer; // 定义链表指针typedef struct list_node{ // 定义链表结构int data;list_pointer link;}list_node;// 用到的操作函数:list_pointer create(); // 建立一个单向链表void insert(list_pointer *p_ptr, list_pointer node); // 在 node 后加入一个新的节点void delete_node(list_pointer *p_ptr, list_pointer trail, list_pointer node);// 删除前一个节点是 trail 的当前节点 nodevoid print(list_pointer ptr); // 打印链表节点中的值list_pointer invert(list_pointer lead); // 反转链表int main(){list_pointer ptr=NULL;list_pointer node, trail;list_pointer *p = ptr;int choose, location, i;printf("you should create a link first:\n");// 建立一个单向链表:ptr=create(); /* ptr 指向链表的第一个节点 */print(ptr);// 根据用户的不同选择进行相应的操作:printf("input number 0, you can quit the program\n");printf("input number 1, you can insert a new node to link\n");printf("input number 2, you can delete a node from the link\n");printf("input number 3, you can invert the link\n");printf("please input your choice\n");scanf("%d", choose);while(choose!=0){switch(choose){case 1:printf("you will insert a node to the link\n");printf("please input the location of the node:\n");scanf("%d", location);node = ptr;i = 1;while(ilocation){node = node-link;i++;}insert(p, node); /* p 为指向 ptr 的指针 */print(ptr);break;case 2:printf("you will delete a node from the link\n");printf("please input the location of the node:\n");scanf("%d", location);node = ptr;if(location ==1)trail = NULL;trail = ptr;i = 1;while(ilocation){trail = trail-link;i++;}node = trail-link;delete_node(p, trail, node);print(ptr);break;case 3:printf("you will invert the link\n");ptr = invert(ptr);print(ptr);break;default:break;return -1;}printf("please input your choice\n");scanf("%d", choose);}return 0;}// 根据用户的输入数值建立一个新的单向链表:list_pointer create(){int i, current, length;list_pointer p1, p2, head;printf("please input the node number of the link:\n");scanf("%d", length);printf("the number of the link is : %d\n", length);printf("please input the data for the link node:\n");i =0;p1= p2= (list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node));head = p1;for(i = 0; iscanf("%d", ¤ t);p1-data = current;p2-link = p1;p2 = p1;p1 = (list_pointer) malloc(sizeof(list_node));}p2-link = NULL;return head;}……( 1 )画出主函数 main 的控制流程图。( 10 分)( 2 ) 设计一组测试用例 , 尽量使 main 函数的语句覆盖率能达到 100% 。 如果认为该函数的语句覆盖率无法达到 100% ,需说明原因。( 8 分)
以下程序的功能是:建立一个带布头结点的单向链表,并将存储在数组中的字符依次存储到链表的各个结点中,请从与下划线处号码对应的一组选项中选择出正确的选项#include <stdlib.h>struct node{char data; struct node *next;};(48) CreatList(char*s),{struct node *h,*p,*q;h=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p=q=h;while(*s!="\0"){ p=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data= (49) ;q->next=p;q= (50) ;s++;}p->next="\0";return h;}main(){ char str[]="link list";struct node*head;head=CreatList(str);…}(1)A.char*B.struct nodeC.struct node*D.char
以下程序中函数fun的功能是:构成一个如图所示的带头结点的单词链表,在结点的数据域中放入了具有两个字符的字符串。函数disp的功能是显示输出该单链表中所有结点中的字符串。请填空完成函数disp。[*]include<stdio.h>typedef struct node /*链表结点结构*/{char sub[3];struct node *next;}Node;Node fun(char s) /*建立链表*/{ … }void disp(Node *h){ Node *
以下程序实现栈的入栈和出栈的操作。其中有两个类:一个是节点类node,它包含点值和指向上一个节点的指针 prev;另一个类是栈类 stack, 它包含栈的头指针 top。生成的链式栈如下图所示。〈IMG nClick=over(this) title=放大 src="tp/jsj/2jc++j28.1.gif"〉下面是实现程序,请填空完成此程序。include 〈iostream〉using namespace std;class stack;class node{int data;node *prev;public:node(int d, node *n){data=d;prev=n;}friend class stack;};class stack{node *top; //栈头public:stack(){top=0;}void push(int i){node *n=【 】;top=n;}int pop(){node *t=top;if (top){top=top-〉prev;int c= t-〉data;delete t;return c;}return 0;}int main (){stack s;s.push(6);s.push(3);s.push (1);return 0;}
已知bead指向一个带头结点的单向链表,链表中每个结点包含数据域(data)和指针域(next),数据域为整型。以下函数求出链表中所有连接点数据域的和值作为函数值返回。请在横线处填入正确内容。{ int data; struct link *next;}main(){ struct link *head;sam(______);{stmct link *p;int s=0;p=head->next;while(p){s+=p->data;p=p->next;}return(s);}
请补充函数fun(),该函数的功能是建立一个带头结点的单向链表并输出到文件“out98.dat”和屏幕上,各结点的值为对应的下标,链表的结点数及输出的文件名作为参数传入。注意:部分源程序给出如下。请勿改动主函数main 和其他函数中的任何内容,仪在函数fun()的横线上填入所编写的若干表达式或语句。试题程序:include<stdio. h>include<conio. h>include<stdlib. h>typedef struct ss{int data;struct ss *next;} NODE;void fun(int n,char*filename){NODE *h,*p, *s;FILE *pf;int i;h=p= (NODE *) malloc (sizeof (NODE));h->data=0;for (i=1; i {s=(NODE *)malloc (sizeof (NODE));s->data=【 】;【 】;p=【 】}p->next=NULL;if ( (pf=fopen (filename, "w") ) ==NULL){printf {"Can not open out9B.clat! ");exit (0);}p=h;fprintf (pf, "\n***THE LIST***\n");print f ("\n***THE LIST***\n")while (p){fprintf (pf, "%3d", p->data)printf ("%3d",p->data);if (p->next ! =NULL){fprintf (pf, "->");printf ("->");}p=p->next;}fprintf (pf, "\n");printf ("\n");fclose (pf);p=h;while (p){s=p;p=p->next;free (s);}}main(){char * filename="out98. dat";int n;clrscr ();printf (" \nInput n: ");scanf ("%d", n);fun (n, filename);}
阅读下列程序说明和C程序,已知其输出为“1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10”。将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。[说明]本程序包含的函数及其功能说明如下:(1)函数first_insert()的功能是在已知链表的首表元之前插入一个指定值的表元;(2)函数reverse_copy()的功能是按已知链表复制出一个新链表,但新链表的表元链接顺序与已知链表的表元链接顺序相反;(3)函数Print_link()用来输出链表中各表元的值;(4)函数free_link()用来释放链表全部表元空间。[程序]include <stdio. h >include <malloe. h >typodef struct node {int val;struct node * next;} NODE;void first_insert(NODE * * p,int v){ NODE *q = (NODE *) malloe(sizeof(NODE));q-val = v; q->next = *p; /* 为新表元赋值*/* p =(1); }NODE * reverse_copy( NODE * p){ NODE * u;for(u=NULL; p!=NULL; p=p->next) first_insert((2));return u;}void printlink(NODE * p ){ for(;(3)) prinff("%d\t", p-val);printf(" \n");}void free_link( NODE * p){ NODE * u;while(p! =NULL) { u=p-next;free(p);(4); }void main( ) { NODE * link1 , * link2;int i;link1 = NULL;for(i=1; i<= 10; i+ + )first_insert(linkl, i);link2 = reverse_copy(link1 );(5);free_link( linkl ) ;free_link(link2); }
阅读以下说明和C++程序,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。[说明]下面程序实现十进制向其它进制的转换。[C++程序]include"ioStream.h"include"math.h"includetypedef struct node {int data;node*next;}Node;Class Transform.{DUDlic:void Trans(int d,int i); //d为数字;i为进制void print();private:Node*top;};void Transform.:Trans(int d,int i){int m,n=0;Node*P;while(d>0){(1);d=d/i;p=new Node;if(!n){p->data=m;(2);(3);n++;}else{p->data=m;(4);(5);}}}void Transform.:print(){Node*P;while(top!=NULL){p=top;if(p->data>9)cout<<data+55;elsecout<<data;top=p->next;delete p;}}
针对以下C语言程序,请按要求回答问题。已知link. c源程序如下:/*link. c程序对单向链表进行操作,首先建立一个单向链表,然后根据用户的选择可以对其进行插入结点、删除结点和链表反转操作*/include<stdio. h>include<stdlib. h>typedef struct list_node * list_pointer; //定义链表指针typedef struct list_node{ //定义链表结构int data;list_pointer link;}list_node;//用到的操作函数list_pointer create(); //建立一个单向链表void insert(list_pointer * p_ptr,list_pointer node); //在node后加入一个新的结点void delete_node(list_pointer * p_ptr,list_pointer trail,list_pointer node);//删除前一个结点是trail的当前结点nodevoid print(list_pointer * p_ptr); //打印链表结点中的值list_pointer invert(list_pointer lead); //反转链表int main(){list_pointer ptr=NULL;list_pointer node,trail;list_pointer * P=&ptr;int choose,location,i;printf("you should create a link first:\n");//建立一个单向链表prt=create(); //ptr指向链表的第一个结点print(ptr);//根据用户的不同选择进行相应的操作:printf("input number 0,you can quit the program\n");printf("input number 1,you can insert a new node to link\n"):printf("input number 2,you can delete a node from the link\n");printf("input number 3,you can invert the link\n"):printf("please input you choice\n");scanf("%d",&choose);while(choose!=0){switch(choose){case 1:i=1:while(i<location){node=node->link;i++:}insert(p,node); //p为指向ptr的指针print(ptr);break;case 2:printf("you will delete a node from the link\n");printf("please input the location of the node:\n");scanf("%d",location):node=ptr;if(location==1)trail=NULL;trail=ptr;i=1:while(i<location){trail=trail->link:i++:}node=trail->link;delete_node(p,trail,node);print(ptr);break;case 3:printf("you will invert the link\n");ptr=invert(ptr);print(ptr);break;default;break;return -1;}printf("please input you choice\n");scanf("%d". &choose):}return 0;//根据用户的输入值建立一个新的单向链表:list_pointer create(){int i,current,length;list_pointer p1,p2,head;printf("please input the node number of the link:\n");scanf("%d". &length):printf("the number of the link is:%d",length);printf("please input the data for the link node:\n");i=0;p1=p2=(list_pointer)malloc(sizeof(list_node));head=p1;for(i=1;i<length;i++){scanf("%d",&current);p1->data=current;p2->link=p1;p2=p1;p1=(list_pointer)malloc(sizeof(list_node));}p2->link=NULL;return head;}画出主函数main的控制流程图。
函数min()的功能是:在带头结点的单链表中查找数据域中值最小的结点。请填空includestruc 函数min()的功能是:在带头结点的单链表中查找数据域中值最小的结点。请填空include <stdio.h>struct node{ int data;struct node *next;};int min(struct node *first)/*指针first为链表头指针*/{ struct node *p; int m;p=first->next; re=p->data; p=p->next;for( ;p!=NULL;p=【 】)if(p->data<m ) re=p->data;return m;}
以下程序的功能是建立—个带有头结点的单向链表,链表结点中的数据通过键盘输入,当输入数据为-1时,表示输入结束(链表头结点的data域不放数据,表空的条件是ph->next==NULL),请填空。include<stdio.h>struct list { int data;struct list *next;};struct list * creatlist(){ struct list *p,*q,*ph;int a;ph=(struct list *)malloc(sizeof(struct
以下程序的功能是:建立一个带有头结点的甲—向链表,并将存储在数组中的字符依次转存到链表的各个结点中,请从与下划线处号码对应的一组选项中选择出正确的选项。#include <stdlib.h>struct node{ char data; struct node *next: };(1) CreatList(char *s){struct node *h,*p,*q;h = (struct node *)malloc sizeof(struct node));p=q=h;while(*s! ='\0'){p = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof (struct node));p->data = (2) ;q->next = p;q - (3) ;S++;}p->next='\0';return h;}main(){char str[]="link list";struct node *head;head = CreatList(str);}(1)A.char*B.struct nodeC.struct node*D.char
以下程序把三个NODEIYPE型的变量链接成—个简单的链表,并在while循环中输出链表结点数据域中的数据。请填空。include<stdio.h>struct node{ int data;struct node*next;);typedef struct node NODETYPE;main(){ NODETYPEa,b,c,*h,*p;a.data=10;b.data=20;c.data=30;h=a;anext=b;b.next=c;c,next='\0';p=h;while(p){printf("%d,",p->data):【 】;}printf("\n");}
链表题:一个链表的结点结构struct Node{int data ;Node *next ;};typedef struct Node Node ;(1)已知链表的头结点head,写一个函数把这个链表逆序( Intel)
下列给定程序中,是建立一个带头结点的单向链表,并用随机函数为各结点数据域赋值。函数fun的作用是求出单向链表结点(不包括头结点)数据域中的最大值,并且作为函数值返回。请改正程序指定部位的错误,使它能得到正确结果。[注意] 不要改动main函数,不得增行或删行,也不得更改程序的结构。[试题源程序]include<stdio.h>include<stdlib.h>typedef struct aa{int data;struct aa *next;}NODE;fun(NODE *h){int max=-1;NODE *p;/***********found************/p=h;while(p){if(p->data>max)max=p->data;/************found************/p=h->next;}return max;}outresult(int s, FILE *Pf){fprintf(pf, "\nThe max in link: %d\n", s);}NODE *creatlink(int n, int m){NODE *h, *p, *s, *q;int i, x;h=p=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));h->data=9999;for(i=1; i<=n; i++){s=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));s->data=rand()%m; s->next=p->next;p->next=s; p=p->next;}p->next=NULL;return h;}outlink(NODE *h, FILE *pf){NODE *p;p=h->next;fprintf(Pf, "\nTHE LIST:\n\n HEAD");while(P){fprintf(pf, "->%d", P->datA); p=p->next;}fprintf(pf, "\n");}main(){NODE *head; int m;head=cteatlink(12,100);outlink(head, stdout);m=fun(head);printf("\nTHE RESULT"\n");outresult(m, stdout);}
下而程序实现十进制向其他进制的转换。[C++程序]include"ioStream.h"include"math.h"include <conio.h>typedef struct node{int data;node *next;}Node;class Transform{public:void Trans(int d,int i); //d为数字;i为进制void print();private:Node *top;};void Transform.:Trans(int d,int i){int m,n=0;Node *P;while(d>0){(1) ;d=d/i;p=new Node;if(!n){P->data=m;(2) j(3) ;n++;}else{p->data=m;(4) ;(5) ;}}}void Transform.:print(){Node *P;while(top!=NULL){p=top;if(P->data>9)cout<<data+55:elsecout<<data;top=p->next;delete P;}}
以下程序中函数fun的功能是:构成—个如图所示的带头结点的单向链表,在结点的数据域中放入了具有两个字符的字符串。函数disp的功能是显示输出该单向链表中所有结点中的字符串。请填空完成函数disp。include<stdio.h>typedef struct node /*链表结点结构*/{ char sub[3];struct node *next;}Node;Node fun(char s) /* 建立链表*/{ ...... }void disp(Node *h){ Node *p;p=h->next;while([ ]){printf("%s\n",p->sub);p=[ ];}}main(){ Node *hd;hd=fun(); disp(hd);printf("\n");}
以下程序的功能是:建立一个带有头结点的单向链表,并将存储在数组中的字符依次转存到链表的各个结点中,请填空。 #include <stdlib.h> stuct node { char data; struet node * next; }; stntct node * CreatList(char * s) { struet node *h,*p,*q; h = (struct node * ) malloc(sizeof(struct node) ); p=q=h; while( * s! ='\0') { p = (struct node *) malloc ( sizeof(struct node) ); p - > data = ( ) q- >next=p; q=p; a++; p- > next ='\0'; return h; } main( ) { char str[ ]= "link list"; struet node * head; head = CreatList(str);A.*sB.sC.*s++D.(*s)++
设有一个不带头结点的单向链表,头指针为head,结点类型为NODE,每个结点包含一个数据域data和一个指针域next,该链表有两个结点,p指向第二个结点(尾结点),按以下要求写出相应语句。新开辟一个结点,使指针s指向该结点,结点的数据成员data赋值为1。
设有一个不带头结点的单向链表,头指针为head,结点类型为NODE,每个结点包含一个数据域data和一个指针域next,该链表有两个结点,p指向第二个结点(尾结点),按以下要求写出相应语句。删除链表的第一个结点。
问答题下列给定程序是建立一个带头结点的单向链表,并用随机函数为各结点赋值。函数fun()的功能是:将单向链表结点(不包括头结点)数据域为偶数的值累加起来,并作为函数值返回。 请改正函数fun中的错误,使它能得出正确的结果。 注意:部分源程序在文件MODII.C中,不要改动main函数,不得增行或删行,也不得更改程序的结构! 试题程序:#include #include #include typedef struct aa{ int data; struct aa *next;}NODE;int fun(NODE *h){ int sum=0; NODE *p; p=h-next; /*********found*********/ while(p-next) { if(p-data%2==0) sum+=p-data; /*********found*********/ p=h-next; } return sum;}NODE *creatlink(int n){ NODE *h,*p,*s; int i; h=p=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); for(i=1;idata=rand()%16; s-next=p-next; p-next=s; p=p-next; } p-next=NULL; return h;}outlink(NODE *h){ NODE *p; p=h-next; printf("The LIST: HEAD"); while(p) { printf("-%d",p-data); p=p-next; } printf("");}main(){ NODE *head; int sum; system("CLS"); head=creatlink(10); outlink(head); sum=fun(head); printf("SUM=%d",sum);}
问答题设某带头结头的单链表的结点结构说明如下:typedef struct nodel{int data struct nodel*next;}node;试设计一个算法:void copy(node*headl,node*head2),将以head1为头指针的单链表复制到一个不带有头结点且以head2为头指针的单链表中。
问答题设有一个不带头结点的单向链表,头指针为head,结点类型为NODE,每个结点包含一个数据域data和一个指针域next,该链表有两个结点,p指向第二个结点(尾结点),按以下要求写出相应语句。删除链表的第一个结点。