有以下程序:程序的运行结果是( )。A.0B.9C.6D.8
有以下程序: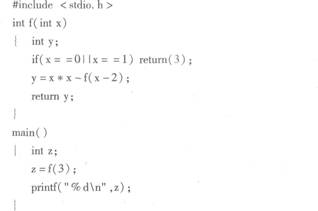 程序的运行结果是( )。
程序的运行结果是( )。
A.0
B.9
C.6
D.8
相关考题:
有以下程序:includeint f(int x){int y;if(x==0||x==1)return(3);y=x*x-f(x-2);return 有以下程序: #include<stdio.h> int f(int x) {int y; if(x==0||x==1)return(3); y=x*x-f(x-2); return y; } main() {int z; z=f(3);printf("%d\n",z); } 程序的运行结果是( )。A.0B.9C.6D.8
有以下程序#include stdio.hint f(int x){ int y;if(x==0||x==1) return(3);y=x*x-f(x-2);return y;}main(){ int z;z=f(3); printf("%d\n",z);}程序的运行结果是A.0B.9C.6D.8
有以下程序includeintf(intx){inty;if(x==0||x==1)return(3);y=x*x-f(x-2);returny;}m 有以下程序 #include <stdio.h> intf(int x) { int y; if(x==0||x==1) return(3); y=x*x-f(x-2); return y; } main() { int z; z=f(3); printf("%d\n",z); } 程序的运行结果是A.0B.9C.6D.8
有以下程序: 程序的运行结果是( )。 A.1 2 3 4B.5 6 7 8C.9 10 11 12S 有以下程序:程序的运行结果是( )。A.1 2 3 4B.5 6 7 8C.9 10 11 12D.1 1 1 1
有下列程序: include int f(int x) { int y; if(x=0‖x==1)r 有下列程序: #include <stdio.h> int f(int x) { int y; if(x=0‖x==1)return(3); y=x*x-f(x-2); return y; } main() { int z; z=f(3);printf("%d\n",z); 程序的运行结果是( )。A.0B.9C.6D.8
有以下程序includeint f(intx){inty; if(x==0||x==1)return(3); y=x*x-f(x-2); return 有以下程序 #include <stdio.h> int f(int x) { int y; if(x==0||x==1) return(3); y=x*x-f(x-2); return y; } main() { int z; z=f(3); printf("%d\n",z); } 程序的运行结果是A.0B.9C.6D.8
有下列程序:#includestdi0.hintf(intx){inty;if(x==0‖x==1)return(3);y=x*x-f(X-2);returny;}voidmain( ){intZ;z=f(3);printf(%d\n,z);}程序的运行结果是( )。A.0B.9C.6D.8
有下列程序: #includestdi0.h intf(intx) { inty; if(x==0‖x==1)return(3); y=x*x-f(X-2); returny; } voidmain( ) { intZ; z=f(3);printf("%d\n",z); } 程序的运行结果是( )。A.0B.9C.6D.8